Dardanelles Army
| Dardanelles Army | |
|---|---|
| Active | First World War Nov.1915– Jan.1916 |
| Country | |
| Branch | |
| Type | Field army |
| Part of | Mediterranean Expeditionary Force |
| Engagements | Gallipoli Campaign |
| Commanders | |
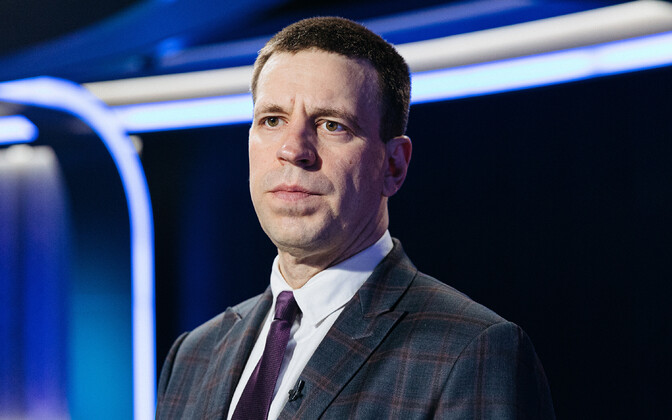
| Notable commanders | William Birdwood |
The Dardanelles Army was a short-lived field army of the British Army during World War I.
History
The Dardanelles Army was formed on 19 November 1915 with headquarters at Imbros and comprised the three army corps of the British Army operating at Gallipoli. It was created as a result of the reorganisation of headquarters when the second Mediterranean front opened at Salonika. Prior to this, all British (and Dominion) units in the Mediterranean came under GHQ of the Mediterranean Expeditionary Force.
The Dardanelles Army was created to manage operations at Gallipoli while the Salonika Army managed operations at Salonika. Both armies came under the direction of the MEF, which was also responsible for the defence of Egypt.[1]
The Dardanelles Army was short-lived as, by the time of its creation, offensive operations at Gallipoli had ceased and plans for the evacuation were being made. For most of its existence, the Army was commanded by Lieutenant General William Birdwood. The Dardanelles Army was disbanded after the final evacuation of the Peninsula in January 1916.[2]
Composition
- British VIII Corps (Lieutenant-General Francis Davies)
- British IX Corps (Lieutenant-General Julian Byng)
- Australian and New Zealand Army Corps (Lieutenant-General Alexander Godley)
- 1st Newfoundland Regiment (Lieutenant-Colonel Arthur Lovell Hadow).[3]
References
- ^ Arthur Butler (1938). "Gallipoli, Palestine and New Guinea (2nd edition), Chapter XX – The Evacuation of Gallipoli" (PDF). Official History of the Australian Army Medical Services, 1914–1918. p. 437. Retrieved 2025-11-30.
- ^ Heathcote, Tony (1999). The British Field Marshals 1736–1997. Barnsley (UK): Pen & Sword. p. 44. ISBN 0-85052-696-5.
- ^ "Gallipoli – 1915". Royal Newfoundland Regiment Museum. Retrieved 2025-12-09.