Welcome to the Czech Portal!
Vítejte na Českém portálu!

|

|

| |
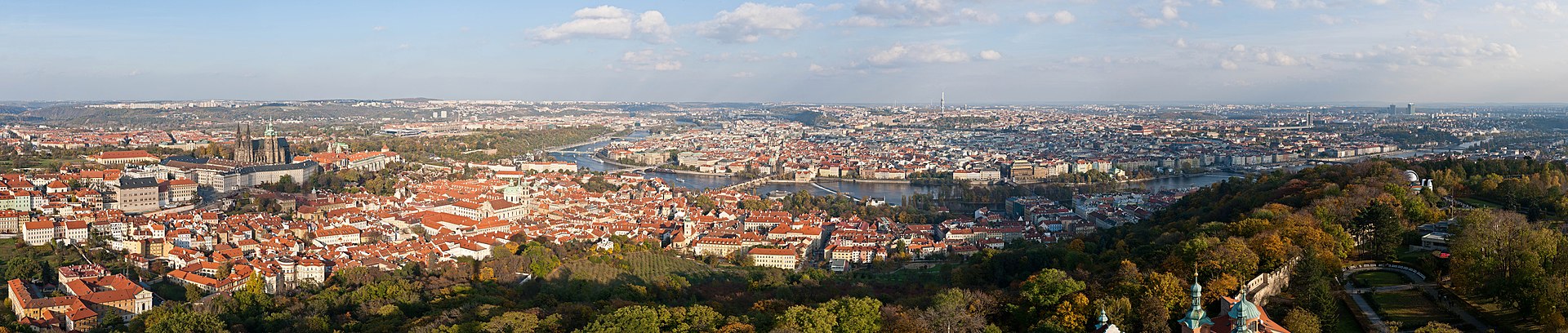
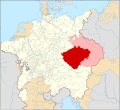
The Czech Republic, also known as Czechia, and historically known as Bohemia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. The country is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the southeast. The Czech Republic has a hilly landscape that covers an area of 78,871 square kilometers (30,452 sq mi) with a mostly temperate continental and oceanic climate. The capital and largest city is Prague; other major cities and urban areas include Brno, Ostrava, Plzeň and Liberec.
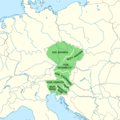
The Duchy of Bohemia was founded in the late 9th century under Great Moravia. It was formally recognized as an Imperial Estate of the Holy Roman Empire in 1002 and became a kingdom in 1198. Following the Battle of Mohács in 1526, all of the Lands of the Bohemian Crown were gradually integrated into the Habsburg monarchy. Nearly a hundred years later, the Protestant Bohemian Revolt led to the Thirty Years' War. After the Battle of White Mountain, the Habsburgs consolidated their rule. With the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire in 1806, the Crown lands became part of the Austrian Empire.
In the 19th century, the Czech lands became more industrialized; further, in 1918, most of the country became part of the First Czechoslovak Republic following the collapse of Austria-Hungary after World War I. Czechoslovakia was the only country in Central and Eastern Europe to remain a parliamentary democracy during the entirety of the interwar period. After the Munich Agreement in 1938, Nazi Germany systematically took control over the Czech lands. Czechoslovakia was restored in 1945 and three years later became an Eastern Bloc communist state following a coup d'état in 1948. Attempts to liberalize the government and economy were suppressed by a Soviet-led invasion of the country during the Prague Spring in 1968. In November 1989, the Velvet Revolution ended communist rule in the country and restored democracy. On 31 December 1992, Czechoslovakia was peacefully dissolved, with its constituent states becoming the independent states of the Czech Republic and Slovakia.
The Czech Republic is a unitary parliamentary republic and developed country with an advanced, high-income social market economy. It is a welfare state with a European social model, universal health care and free-tuition university education. It ranks 32nd in the Human Development Index. The Czech Republic is a member of the United Nations, NATO, the European Union, the OECD, the OSCE, the Council of Europe and the Visegrád Group. (Full article...)
Selected article -
Leitmeritz was the largest subcamp of the Flossenbürg concentration camp, operated by Nazi Germany in Leitmeritz, Reichsgau Sudetenland (now Litoměřice, Czech Republic). Established on 24 March 1944 as part of an effort to disperse and increase war production, its prisoners were forced to work in the caverns Richard I and II, producing Maybach HL230 tank engines for Auto Union (now Audi) and preparing the second site for intended production of tungsten and molybdenum wire and sheet metal by Osram. Of the 18,000 prisoners who passed through the camp, about 4,500 died due to disease, malnutrition, and accidents caused by the disregard for safety by the SS staff who administered the camp. In the last weeks of the war, the camp became a hub for death marches. The camp operated until 8 May 1945, when it was dissolved by the German surrender. (Full article...)
Selected picture

Photographer: NASA; License: Public domain
In this month
- 2 March 1978 – Vladimír Remek becomes the first man in space from a country other than the United States and USSR
- 6 March 1645 – One of the bloodiest battles of the Thirty Years' War, the Battle of Jankau takes place 50km from Prague
- 16 March 1939 – The Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia is established following the end of the Second Czechoslovak Republic
- 29 March 1896 – The first Prague derby is played between Sparta and Slavia. The match ends 0–0
- 30 March 1968 – Ludvík Svoboda (pictured) is elected President of Czechoslovakia
Categories
Selected biography -

Gregor Johann Mendel OSA (/ˈmɛndəl/; Czech: Řehoř Jan Mendel; 20 July 1822 – 6 January 1884) was an Austrian biologist, meteorologist, mathematician, Augustinian friar and abbot of St. Thomas' Abbey in Brno (Brünn), Margraviate of Moravia. Mendel was born in a German-speaking family in the Silesian part of the Austrian Empire (today's Czech Republic) and gained posthumous recognition as the founder of the modern science of genetics. Though farmers had known for millennia that crossbreeding of animals and plants could favor certain desirable traits, Mendel's pea plant experiments conducted between 1856 and 1863 established many of the rules of heredity, now referred to as the laws of Mendelian inheritance.
Mendel worked with seven characteristics of pea plants: plant height, pod shape and color, seed shape and color, and flower position and color. Taking seed color as an example, Mendel showed that when a true-breeding yellow pea and a true-breeding green pea were cross-bred, their offspring always produced yellow seeds. However, in the next generation, the green peas reappeared at a ratio of 1 green to 3 yellow. To explain this phenomenon, Mendel coined the terms "recessive" and "dominant" in reference to certain traits. In the preceding example, the green trait, which seems to have vanished in the first filial generation, is recessive, and the yellow is dominant. He published his work in 1866, demonstrating the actions of invisible "factors"—now called genes—in predictably determining the traits of an organism. (Full article...)
Did you know?
- ...that, although Mozart never visited Kroměříž, much of the Academy Award-winning film Amadeus was filmed at the local episcopal residence?
- ... that in 2013, the Czech Republic plans to directly elect its president for the first time in its history?
- ... that footballer Petr Vrabec won six Czechoslovak league titles with Sparta Prague?
- ... that a 1926 voyage to Java inspired Czech poet Konstantin Biebl for the remainder of his life?
General images
Related portals
Topics

Czech lands: Bohemia • Moravia • Czech Silesia
History: Únětice culture • Boii • Marcomanni • Samo • Great Moravia • Přemyslid dynasty • Lands of the Bohemian Crown • Czech lands (1526–1648) • 1648–1867 • 1867–1918) • Czechoslovakia • Czech Republic
Geography: Lakes • Protected areas • Regions • Rivers
Law: Judiciary • Law enforcement • Supreme Court of the Czech Republic
Politics: Administrative divisions • Government • Constitution • Elections • Foreign relations • Army • Parliament • Political parties • President • Prime Minister
Economy: Banks • Czech koruna • Energy • Oil and gas deposits • Stock Exchange • Tourism • Transport
Culture: Architecture • Art • Cinema • Cuisine • Demographics • Education • Language • Literature • Media • Music • Philosophy • Prostitution • Public holidays • Religion • Sport • Television • Video games
Symbols: Flag • Coat of arms • National anthem (Kde domov můj)
Lists: Outline of the Czech Republic • List of Czech Republic–related topics
WikiProjects
Featured and good content
Things to do
Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
 Commons
Commons
Free media repository -
 Wikibooks
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
 Wikidata
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
 Wikinews
Wikinews
Free-content news -
 Wikiquote
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
 Wikisource
Wikisource
Free-content library -
 Wikiversity
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
 Wikivoyage
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
 Wiktionary
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
-

-

-

-

-
Random portal