Balls 8
| Balls 8 | |
|---|---|
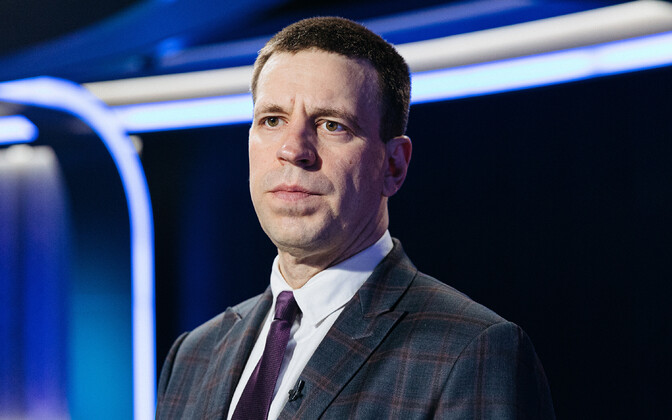
 A NASA TF-104G (below) flies chase on the NB-52B Balls 8 (above) on 14 September 1979. | |
| General information | |
| Type | Boeing NB-52B Stratofortress |
| Manufacturer | Boeing Aircraft Company |
| Status | Retired |
| Owners | United States Air Force NASA |
| Serial | 52-008 |
| History | |
| First flight | 11 June 1955 |
| In service | June 8, 1959 |
| Preserved at | Edwards Air Force Base, California |



Balls 8 is a NASA Boeing NB-52B mothership which was retired in 2004 after almost 50 years of flying service with NASA.[1][2] The aircraft is famous for dropping the X-15 aerospace research vehicle on 106 of the 199 X-15 program flights.[3]
Introduction
Boeing NB-52B Stratofortress, Air Force 52-0008, has operated from Edwards Air Force Base for 45 years.[4] The goal of launching the North American X-15 hypersonic research aircraft project in 1958 took the NB-52B and its sister ship, the NB-52A, 52-0003.[4] The NB-52B served as a launch platform for numerous programs until its final mission on 16 November 2004, whereas the NB-52A was retired in October 1969.[4]
Operating as a flying launch pad nine miles (14 km) above the ground, it had to provide the rocket planes it carried with the propellants, gasses, and power typically associated with a ground based launch pad. Because of this capability, the airplane became a vital tool for aeronautical studies.[5]
The right wing of the Stratofortress was reinforced and fitted with a pylon that could carry the heaviest payloads ever launched from an airplane's wing—more than 50,000 pounds (23,000 kg) (about 1⁄5 of the aircraft's own weight).[6]
The Stratofortress' X-15 rocket aircraft flew pilots to unprecedented altitudes and speeds. The first winged vehicles reached speeds of Mach 1, Mach 2, Mach 3, and Mach 4, respectively. They also flew for the first time over 130,000 feet (40,000 m), and eventually reached more than 364,000 feet (111,000 m) above the surface of the Earth.[4] Five pilots earned astronaut wings by flying more than 50 miles (80 km) in an X-15. Unfortunately, one of those pilots was killed on a qualifying flight when the third X-15 blew up on re-entry.[4]
The re-engineered Stratofortress NB-52B was also used during the development of the Space Shuttle program, launched a number of wingless lifting body aircraft that showed the feasibility of the Space Shuttle's steep gliding approach to landings. The new NB-52B showed that an airplane weighing 3.5 million pounds (1.6 kt) could also do such landings. The parachutes that dropped the Shuttle's solid fuel boosters to the ocean were also tested in drops from a pylon on the aircraft's wing.[4] The drag chute that slowed the Space Shuttle down after landing was also tested on this aircraft.[4]
Despite increasing maintenance costs, the unique abilities of the NB-52B were still required by new programs, launching a number of scale RPAVs and drones in the 1970s and 1980s, including the 3⁄8 scale F-15 RPAV (Remotely Piloted Research Vehicle), the Ryan Firebee II (Ryan Firebee) drone (Ryan Firebee based Drone for Aeroelastic Structure Testing (DAST)), and the highly maneuverable aircraft technology (HiMAT).[4]
It was the last B-52 with a bomb bay configured to carry the MAU-12 bomb rack originally used to drop large thermonuclear warheads.[4]
For research purposes, the NB-52B itself was utilized. By flying past a tower equipped with smoke generators, it helped researchers visualize the wake turbulence of a large aircraft. It served as an air-to-air gunnery target. In the mid-1990s, when the NB-52B was testing pollution reducing fuel additives with a pair of jet engines mounted under the bomb bay, it flew as a ten engine jet for some time.[4]
During the X-38 program, the biggest parafoil in history has been dropped from NB-52B.[4] The parafoil had an area of 7,500 square feet, greater than 1-1/2 times the area of the wing on a Boeing 747.[4]
The final program that utilised the NB-52Bs with the launch of the world's most powerful airbreathing jet engine. On its final mission it launched the third X-43A Hyper-X supersonic combustion ramjet on a modified Pegasus booster that propelled it to a speed of Mach 9.6 (7,365 mph or 11,853 km/h) at an altitude of 110,000 feet (34,000 m).[4] Future aerospace vehicles with a speed of more than 4,300 miles per hour (7,000 km/h) are presaged by the successful operation of supersonic combustion ramjet engine.
On 17 December 2004, the NB-52B was honored with a retirement ceremony at NASA Dryden Flight Research Center in Edwards Air Force Base.[5]
History
Balls 8 was originally an RB-52B[2] that was first flown on 11 June 1955, and entered service with NASA on 8 June 1959. It was modified at North American Aviation's Palmdale facility to enable it to carry the X-15. As on its NB-52A predecessor, a pylon was installed beneath the right wing between the fuselage and the inboard engines with a 6-by-8-foot (1.8 m × 2.4 m) section removed from the wing flap to accommodate the X-15's tail.
The modified bomber flew 159 captive-carry and launch missions for the X-15 program from June 1959 until October 1968. It was first used to launch the X-15 on its fifth flight, 23 January 1960. It also flew missions for the X-24, HiMAT, lifting body vehicles, X-43, early launches of the OSC Pegasus rocket, and numerous other programs.
At its retirement on 17 December 2004, Balls 8 was the oldest active B-52 in service, and the only active B-52 that was not an H model. It also had the lowest total airframe time of any operational B-52. It is on permanent public display near the north gate of Edwards Air Force Base in California.[2]
It derives its nickname from its NASA tail number 52-008: leading zeroes plus the number 8. Among USAF personnel, it is common practice to refer to aircraft whose tail number contains two or more zeros as "Balls" and the last digit (or two digits) of its tail number.
See also
- The High and Mighty One, NB-52A serial number 52-003, is the other launch aircraft used for X-15 flights. It is on display at the Pima Air & Space Museum next to Davis-Monthan AFB in Tucson, Arizona (32°8′28.00″N 110°52′11.62″W / 32.1411111°N 110.8698944°W).
- B-52B, serial number 52-005, can be seen at the Wings Over the Rockies Museum's B-52B "005",[7] Denver, Colorado.
- List of NASA aircraft
- Cosmic Girl, a Boeing 747-41R in use by Virgin Orbit as a mothership for the Mark II LauncherOne rocket
- Stargazer, a modified Lockheed L-1011 TriStar used as a mothership for Northrop Grumman Pegasus and Pegasus XL rockets
References
- ^ Creech, Gray (15 December 2004). "End of an Era: NASA's Famous B-52B Retires". NASA Dryden Flight Research Center. Archived from the original on 28 December 2004.
- ^ a b c Gibbs, Yvonne, ed. (28 February 2014). "NASA Armstrong Fact Sheet: B-52B "Mothership" Launch Aircraft". NASA. Archived from the original on 18 March 2022.
- ^ Engel, Hans-Peter (24 February 2000). "X-15 - Hypersonic Research at the Edge of Space". NASA History.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m "Balls_Eight_History_of_the_Boeing_NB-52B_Stratofortress_Mothership_eBook". www.air-and-space.com. Retrieved 30 April 2024.
- ^ a b Richmond, Jeff (23 August 2016). "Balls Eight - The B-52 That Was The Mother of Mother Ships". Avgeekery.com. Retrieved 30 April 2024.
- ^ Creech, Gray (15 December 2004). "End of an Era: NASA's Famous B-52B Retires". NASA Dryden Flight Research Center. Archived from the original on 28 December 2004.
- ^ "Boeing B-52B Stratofortress". Wings Over the Rockies Air & Space Museum. Retrieved 1 January 2015.
Further reading
- Lockett, Brian (2009). Balls Eight: History of the Boeing NB-52B Stratofortress Mothership. LockettBooks. ISBN 978-1-329-09564-9. OCLC 1256691010.