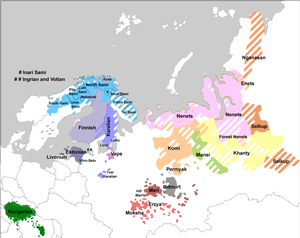
Selkup is the language of the Selkups, belonging to the Samoyedic group of the Uralic language family. It is spoken by some 1,570 people (1994 est.) in the region between the Ob and Yenisei Rivers (in Siberia). The language name Selkup comes from the Russian селькуп, based on the native name used in the Taz dialect, шӧльӄумыт әты (šöľqumyt əty lit. 'forest-man language'). Different dialects use different names.
Selkup is fractured in an extensive dialect continuum whose ends are no longer mutually intelligible. The three main varieties are the Taz (Northern) dialect (тазовский диалект, tazovsky dialekt), which became the basis of the Selkup written language in the 1930s, Tym (Central) dialect (тымский диалект, tymsky dialekt), and Ket dialect (кетский диалект, ketsky dialekt). It is not related to the Ket language.
Grammar
Southern Selkup
Noun
| Case name | Ending | Meaning | Example | Meaning of the example | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nominative case | ∅ | subject | маҗь | forest (as a subject) | |
| Accusative case | -п, -м (rare) | direct object | ма́җеп | forest (as an object) | |
| Genitive case | -т, -н (rare) | possession | ма́җет | of a forest | |
| Dative case | animate | -н | indirect object (animate) | ӄун, ӄумн | to the person |
| inanimate | -нд | indirect object (inanimate) | маҗӧ́нд | to the forest | |
| Inessive case | animate | -нан | the X has | ӄу́нан | the person has |
| inanimate | -ӷэт/-ӄэт | in | маҗӧ́ӷэт | in the forest | |
| Elative case | -эутэ/-утэ | out of, from, along | маҗӧ́утэ | out of the forest | |
| Instrumental-comitative case | -ӽе/-хе, -э́ (with nouns denoting means of transport, always stressed) | with | маҗьӽе́ | with the forest | |
| Abessive case | -галк/-калк | without | маҗьга́лк | without the forest | |
| Translative case | -тӄо | into | маҗетӄо́ | [turn] into a forest | |
| Exessive case[a] | animate | -ндо/-эндо | from | ку́ндо | from the person |
| inanimate | -ӷэндо/-ӄэндо | from | маҗӧ́ӷэндо | from the forest | |
- ^ Almost out of use[citation needed]
References
- ^ "Итоги Всероссийской переписи населения 2020 года. Таблица 6. Население по родному языку" [Results of the All-Russian population census 2020. Table 6. population according to native language.]. rosstat.gov.ru. Retrieved 2023-01-03.
- ^ Rantanen, Timo; Tolvanen, Harri; Roose, Meeli; Ylikoski, Jussi; Vesakoski, Outi (2022-06-08). "Best practices for spatial language data harmonization, sharing and map creation—A case study of Uralic". PLOS ONE. 17 (6): e0269648. Bibcode:2022PLoSO..1769648R. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0269648. PMC 9176854. PMID 35675367.
- ^ Rantanen, Timo, Vesakoski, Outi, Ylikoski, Jussi, & Tolvanen, Harri. (2021). Geographical database of the Uralic languages (v1.0) [Data set]. Zenodo. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4784188
- ^ Korotkih, Grigoriy V. (2022). Современный язык нарымских селькупов (PDF) (in Russian). Соиздательство ценных книг «Грасион». p. 150. ISBN 978-5-6046304-5-7.
Works cited
- Helimski, Eugene (1998). "Selkup". In Abondolo, David (ed.). The Uralic Languages. London: Routledge. pp. 548–579. ISBN 0-415-08198-X.









You must be logged in to post a comment.