Chemical compound
Leukotriene D4 (LTD4) is one of the leukotrienes. Its main function in the body is to induce the contraction of smooth muscle, resulting in bronchoconstriction and vasoconstriction. It also increases vascular permeability. LTD4 is released by basophils. Other leukotrienes that function in a similar manner are leukotrienes C4 and E4. Pharmacological agents that inhibit the function of these leukotrienes are leukotriene receptor antagonists (e.g., zafirlukast, montelukast) and are useful for asthmatic individuals.[1]
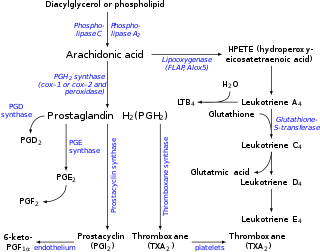 Eicosanoid synthesis. (Leukotrienes at right.)
Eicosanoid synthesis. (Leukotrienes at right.)
References
|
|---|
Receptor
(ligands) | | BLTTooltip Leukotriene B4 receptor | | BLT1Tooltip Leukotriene B4 receptor 1 | |
|---|
| BLT2Tooltip Leukotriene B4 receptor 2 | |
|---|
|
|---|
| CysLTTooltip Cysteinyl leukotriene receptor | | CysLT1Tooltip Cysteinyl leukotriene receptor 1 | |
|---|
| CysLT2Tooltip Cysteinyl leukotriene receptor 2 | |
|---|
| CysLTETooltip Cysteinyl leukotriene receptor E | |
|---|
|
|---|
|
|---|
Enzyme
(inhibitors) | | 5-LOXTooltip Arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase | |
|---|
| 12-LOXTooltip Arachidonate 12-lipoxygenase | |
|---|
| 15-LOXTooltip Arachidonate 15-lipoxygenase | |
|---|
| LTA4HTooltip Leukotriene A4 hydrolase | |
|---|
| LTB4HTooltip Leukotriene B4 ω-hydroxylase | |
|---|
| LTC4STooltip Leukotriene C4 synthase | |
|---|
| LTC4HTooltip Leukotriene C4 hydrolase | |
|---|
| LTD4Tooltip Leukotriene D4 hydrolase | |
|---|
|
|---|
| Others | |
|---|
|










You must be logged in to post a comment.