Isobucaine is a local anesthetic.[1]
Synthesis
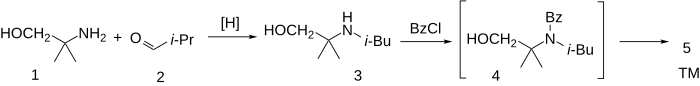
The reductive amination between aminomethyl propanol (1) and isobutanal [78-84-2] (2) afforded N-Isobutyl-1,1-dimethyl-2-hydroxyethanamine, CID:18315986 (3). Acylation of the amine with benzoyl chloride [98-88-4] hypothetically goes initially to the amide (4'). The acid catalysis used in the reaction leads to an N to O acyl migration to afford isobucaine (5).
See also
References
- ^ Thoma KH (1961). Accepted Dental Remedies (26th ed.). Chicago: American Dental Association. p. 30.
- ^ Reasenberg JR, Goldberg SD (June 1945). "Esters of β-Alkylaminoethanols". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 67 (6): 933–939. doi:10.1021/ja01222a017.












