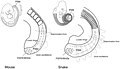
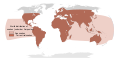
The Snake PortalSnakes are elongated limbless reptiles of the suborder Serpentes (/sɜːrˈpɛntiːz/). Cladistically squamates, snakes are ectothermic, amniote vertebrates covered in overlapping scales much like other members of the group. Many species of snakes have skulls with several more joints than their lizard ancestors and relatives, enabling them to swallow prey much larger than their heads (cranial kinesis). To accommodate their narrow bodies, snakes' paired organs (such as kidneys) appear one in front of the other instead of side by side, and most only have one functional lung. Some species retain a pelvic girdle with a pair of vestigial claws on either side of the cloaca. Lizards have independently evolved elongate bodies without limbs or with greatly reduced limbs at least twenty-five times via convergent evolution, leading to many lineages of legless lizards. These resemble snakes, but several common groups of legless lizards have eyelids and external ears, which snakes lack, although this rule is not universal (see Amphisbaenia, Dibamidae, and Pygopodidae). Living snakes are found on every continent except Antarctica, and on most smaller land masses; exceptions include some large islands, such as Ireland, Iceland, Greenland, and the islands of New Zealand, as well as many small islands of the Atlantic and central Pacific oceans. Additionally, sea snakes are widespread throughout the Indian and Pacific oceans. Around thirty families are currently recognized, comprising about 520 genera and about more than 4,170 species. They range in size from the tiny, 10.4 cm-long (4.1 in) Barbados threadsnake to the reticulated python of 6.95 meters (22.8 ft) in length. The fossil species Titanoboa cerrejonensis was 12.8 meters (42 ft) long. Snakes are thought to have evolved from either burrowing or aquatic lizards, perhaps during the Jurassic period, with the earliest known fossils dating to between 143 and 167 Ma ago. The diversity of modern snakes appeared during the Paleocene epoch (c. 66 to 56 Ma ago, after the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event). The oldest preserved descriptions of snakes can be found in the Brooklyn Papyrus. (Full article...) Selected article - The evolutionary history of snake venom is a matter of debate. Historically, snake venom was believed to have evolved once, at the base of the Caenophidia, or derived snakes. Molecular studies published beginning in 2006 suggested that venom originated just once among a putative clade of reptiles, called Toxicofera, approximately 170 million years ago. Under this hypothesis, the original toxicoferan venom was a very simple set of proteins that were assembled in a pair of glands. Subsequently, this set of proteins diversified in the various lineages of toxicoferans, including Serpentes, Anguimorpha, and Iguania: several snake lineages also lost the ability to produce venom. The Toxicoferan hypothesis was challenged by studies in the mid-2010s, including a 2015 study which found that venom proteins had homologs in many other tissues in the Burmese python. The study therefore suggested that venom had evolved independently in different reptile lineages, including once in the Caenophid snakes. Venom containing most extant toxin families is believed to have been present in the last common ancestor of the Caenophidia: these toxins subsequently underwent tremendous diversification, accompanied by changes in the morphology of venom glands and delivery systems. (Full article...) Did you know (auto-generated) -
More did you know? -
Quality ContentFeatured snake-related articles - George Went Hensley - List of snakes of Trinidad and Tobago Good snake-related articles - Agkistrodon piscivorus - Bitis arietans - Bitis gabonica - Black mamba - Black-necked spitting cobra - Eastern green mamba - Forest cobra - Hydrophiinae - Many-banded krait - Nerodia clarkii - Russell's viper - Snake scales - Vipera berus - Western green mamba TopicsLists - List of snakes by common name - List of Serpentes families - List of snake genera - List of dangerous snakes
Families - Acrochordidae - Aniliidae - Anomochilidae - Boidae - Bolyeriidae - Colubridae - Cylindrophiidae - Elapidae - Loxocemidae - Pythonidae - Tropidophiidae - Uropeltidae - Viperidae - Xenopeltidae - Anomalepididae - Leptotyphlopidae - Typhlopidae Anatomy and physiology - Infrared sensing in snakes - Pelvic spur - Snake scales - Snake skeleton SubcategoriesRelated portalsNeed help?Do you have a question about Snakes that you can't find the answer to? Consider asking it at the Wikipedia reference desk. Snakes in the newsNo recent news Things you can do
Help at WikiProjects:
Associated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
Discover Wikipedia using portals |
Värsked postitused
- Grauberg Lepik liitus Islandi kõrgliigaklubiga
- Espordi grupisõidus krooniti Eesti meistriteks Kivistik ja Klais-Peets
- Politsei: Gene Hackmani ja tema abikaasa surnukehad olid juba lagunema hakanud
- Trump kiitis Ühendkuningriiki Brexiti eest, sai küllakutse kuningalt
- VIDEO: Trump ei usu, et ütles, et Zelenski on diktaator