| Main page | Maps |
The Maps and Cartography Portal
A map is a symbolic depiction of interrelationships, commonly spatial, between things within a space. A map may be annotated with text and graphics. Like any graphic, a map may be fixed to paper or other durable media, or may be displayed on a transitory medium such as a computer screen. Some maps change interactively. Although maps are commonly used to depict geographic elements, they may represent any space, real or fictional. The subject being mapped may be two-dimensional such as Earth's surface, three-dimensional such as Earth's interior, or from an abstract space of any dimension.
Maps of geographic territory have a very long tradition and have existed from ancient times. The word "map" comes from the medieval Latin: Mappa mundi, wherein mappa meant 'napkin' or 'cloth' and mundi 'of the world'. Thus, "map" became a shortened term referring to a flat representation of Earth's surface. (Full article...)
Cartography (/kɑːrˈtɒɡrəfi/; from Ancient Greek: χάρτης chartēs, 'papyrus, sheet of paper, map'; and γράφειν graphein, 'write') is the study and practice of making and using maps. Combining science, aesthetics and technique, cartography builds on the premise that reality (or an imagined reality) can be modeled in ways that communicate spatial information effectively. (Full article...)
Selected article -

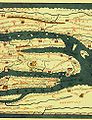
Maps of Jerusalem can be categorised between original factual maps, copied maps and imaginary maps, the latter being based on religious books. The maps were produced in a variety of materials, including parchment, vellum, mosaic, wall paintings and paper. Most extant maps known to scholars from the pre-modern era were prepared by Christian mapmakers for a Christian European audience. All maps marking milestones in the cartography of Jerusalem are listed here following the cartographic histories of the city, from Titus Tobler and Reinhold Röhricht's studies in the 19th century to those of Hebrew University of Jerusalem academics Rehav Rubin and Milka Levy-Rubin in recent decades. The article lists maps that progressed the cartography of Jerusalem before the rise of modern surveying techniques, showing how mapmaking and surveying improved and helped outsiders to better understand the geography of the city. Imaginary maps of the ancient city and copies of existing maps are excluded.
The Madaba Map discovered in modern-day Jordan is the oldest known map of Jerusalem, in the form of a mosaic in a Greek Orthodox Church. At least 12 maps survive from the Catholic mapmakers of the Crusades; they were drawn on vellum and mostly show the city as a circle. Approximately 500 maps are known between the late-1400s and the mid-1800s; the significant increase in number is due to the advent of the printing press. The first printed map of the city was drawn by Erhard Reuwich and published in 1486 by Bernhard von Breydenbach in his Peregrinatio in Terram Sanctam, based on his pilgrimage of 1483. Few of the mapmakers had travelled to Jerusalem – most of the maps were either copies of others' maps or were imaginary (i.e. based on reading of religious texts) in nature. The first map based on actual field measurements was published in 1818 by the Czech mapmaker Franz Wilhelm Sieber. The first map based on modern surveying techniques was published by Charles Wilson in 1864–65 for the British Ordnance Survey. (Full article...)
General images -
Selected quote
| “ | And then I went to bed, and went to sleep, and slept soundly, and the next morning I sent for the chief engineer of the War Department (our map-maker), and I told him to put the Philippines on the map of the United States (pointing to a large map on the wall of his office), and there they are, and there they will stay while I am President! | ” |
| — President William McKinley | ||
Related portals
Related WikiProjects
Selected biography -

Su Song (Chinese: 蘇頌; Pe̍h-ōe-jī: So͘ Siōng, 1020–1101), courtesy name Zirong (Chinese: 子容; Pe̍h-ōe-jī: Chú-iông), was a Chinese polymathic scientist and statesman. Excelling in a variety of fields, he was accomplished in mathematics, astronomy, cartography, geography, horology, pharmacology, mineralogy, metallurgy, zoology, botany, mechanical engineering, hydraulic engineering, civil engineering, invention, art, poetry, philosophy, antiquities, and statesmanship during the Song dynasty (960–1279).
Su Song was the engineer for a hydro-mechanical astronomical clock tower in medieval Kaifeng, which employed an early escapement mechanism. The escapement mechanism of Su's clock tower had been invented by Tang dynasty Buddhist monk Yi Xing and government official Liang Lingzan in 725 AD to operate a water-powered armillary sphere, although Su's armillary sphere was the first to be provided with a mechanical clock drive. Su's clock tower also featured the oldest known endless power-transmitting chain drive, called the tian ti (天梯), or "celestial ladder", as depicted in his horological treatise. The clock tower had 133 different clock jacks to indicate and sound the hours. Su Song's treatise about the clock tower, Xinyi Xiangfayao (新儀象法要), has survived since its written form in 1092 and official printed publication in 1094. The book has been analyzed by many historians, such as the British biochemist, historian, and sinologist Joseph Needham. The clock itself, however, was dismantled by the invading Jurchen army in 1127 AD, and although attempts were made to reassemble it, the tower was never successfully reinstated. (Full article...)
Selected picture
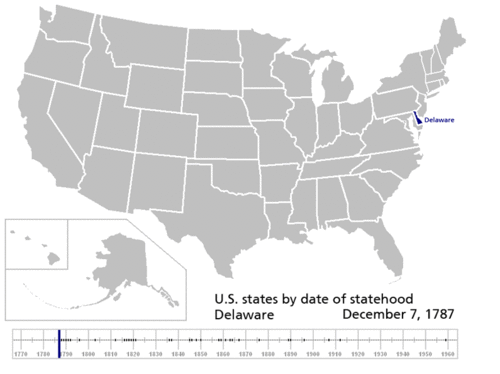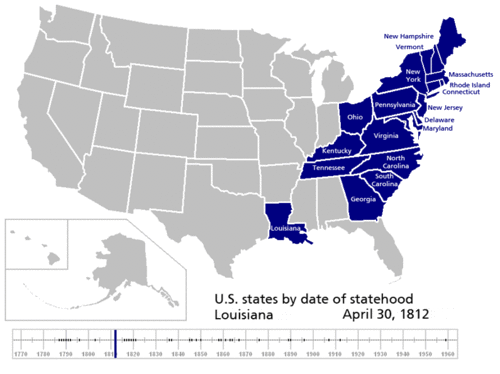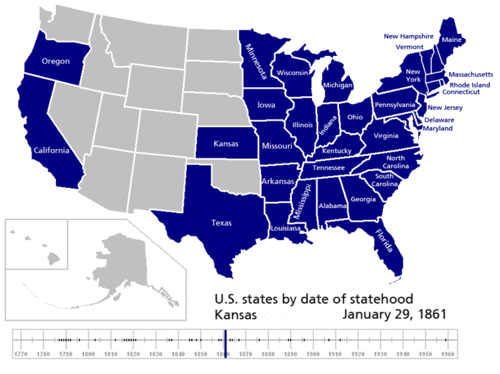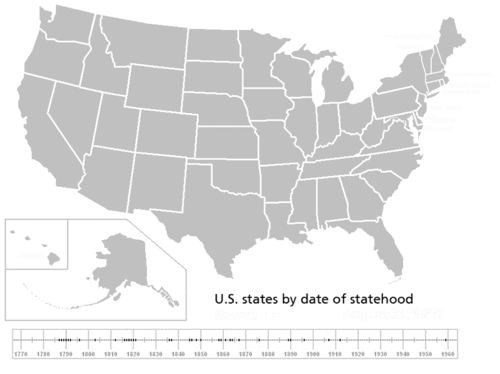
Did you know
- ... that actress Agnes Mapes had to improvise a complex choreographed dance from basic poses for the 1907 play The Holy City?
- ... that Kathryn Maple won the Sunday Times Watercolour Competition twice in three years?
- ... that DeepStateMap.Live, an interactive map of the Russian invasion of Ukraine, received up to 120,000 visitors in 30 minutes during the Battle of Izium in the 2022 Kharkiv counteroffensive?
- ... that the Canadian League for Peace and Democracy organized a 10,000-person rally at Maple Leaf Gardens in Toronto to protest a 2,500-person fascist rally?
- ... that the actress Lottie Williams was one of the cakewalk dancers depicted on the front cover of the sheet music for Scott Joplin's "Maple Leaf Rag"?
- ... that the 100 gecs tree was listed as a "place of worship" on Google Maps?
Topics
Map - Atlas - Geography - Topography
Cartography: Cartographers - History of cartography - Ancient world maps - World maps - Compass rose - Generalization - Geographic coordinate system - Geovisualization - Relief depiction - Scale - Terra incognita - Planetary cartography
Map projection: Azimuthal equidistant - "Butterfly" - Dymaxion - Gall–Peters - General Perspective - Goode homolosine - Mercator - Mollweide - Orthographic - Peirce quincuncial - Robinson - Sinusoidal - Stereographic
Maps: Animated mapping - Cartogram - Choropleth map - Estate map - Geologic map - Linguistic map - Nautical chart - Pictorial map - Reversed map - Road atlas - Thematic map - Topographic map - Weather map - Web mapping - World map
Map examples
Geographic

Political
Nautical
Categories
Things you can do
|
Here are some Geography related tasks you can do:
|
Atlases and maps of the world at Wikimedia Commons
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
 Commons
Commons
Free media repository -
 Wikibooks
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
 Wikidata
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
 Wikinews
Wikinews
Free-content news -
 Wikiquote
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
 Wikisource
Wikisource
Free-content library -
 Wikiversity
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
 Wiktionary
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus