Sulfamide (IUPAC name: sulfuric diamide) is a compound with the chemical formula SO2(NH2)2 and structure H2N−S(=O)2−NH2. Sulfamide is produced by the reaction of sulfuryl chloride with ammonia. Sulfamide was first prepared in 1838 by the French chemist Henri Victor Regnault.[2]
Sulfamide functional group
In organic chemistry, the term sulfamide may also refer to the functional group which consists of at least one organic group attached to a nitrogen atom of sulfamide.
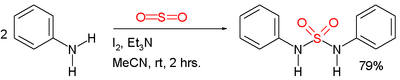
Symmetric sulfamides can be prepared directly from amines, sulfur dioxide gas and an oxidant:[3]
In this example, the reactants are aniline, triethylamine (Et3N, Et = ethyl group), and iodine. Sulfur dioxide is believed to be activated through a series of intermediates: Et3N−+−I−, Et3N−I+−I−3 and Et3N+−SO−2.
The sulfamide functional group is an increasingly common structural feature used in medicinal chemistry.[4]
See also
References
- ^ Merck Index, 11th Edition, 8894.
- ^ Regnault, Victor (1838) "Sur l'acide chlorosulfurique et la sulfamide" (On sulfuryl chloride and sulfamide), Annales de chimie et de physique, series 2, 69 : 170-184; see especially "Action de gaz ammoniac sec sur la liqueur chlorosulfurique" (Action of dry ammonia gas on liquid sulfuryl chloride), pages 176-180.
- ^ Leontiev, A. V.; Dias, H. V. R.; Rudkevich, D. M. (2006). "Sulfamides and sulfamide polymers directly from sulfur dioxide". Chemical Communications. 2006 (27): 2887–2889. doi:10.1039/b605063h. PMID 17007406.
- ^ Reitz, A. B.; Smith, G. R.; Parker, M. H. (2009). "The Role of Sulfamide Derivatives in Medicinal Chemistry: A Patent Review (2006 – 2008)". Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Patents. 19 (10): 1449–1453. doi:10.1517/13543770903185920. PMID 19650745. S2CID 6561685.