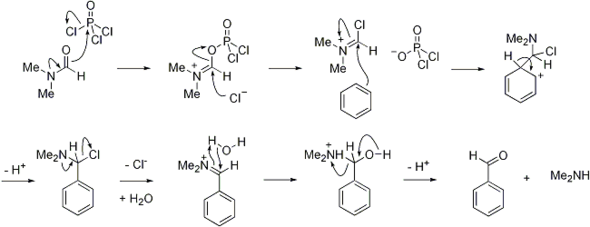
The Vilsmeier reagent is an organic compound with the formula [(CH3)2NCHCl]Cl. It is a salt consisting of the N,N-dimethyliminium cation ([(CH3)2N=CHCl]+) and chloride anion. Depending on the particular reaction, the anion can vary. In typical POCl3-based reactions, the anion is PO2Cl2−. The iminium cation [(CH3)2N=CHCl]+ is the reactive component of interest. This iminium species is a derivative of the imidoyl chloride CH3N=CHCl. Analogues of this particular reagent are generated when tertiary amides other than DMF are treated with POCl3.
The salt is a white solid that is soluble in polar organic solvents. Vilsmeier reagent is the active intermediate in the formylation reactions, the Vilsmeier reaction or Vilsmeier-Haack reaction that use mixtures of dimethylformamide and phosphorus oxychloride to generate the Vilsmeier reagent, which in turn attacks a nucleophilic substrate and eventually hydrolyzes to give formyl. It is a source of "O=CH+".[1]
See also
- Eschenmoser's salt, [(CH3)2NCH2]I
References
- ^ Paul R. Giles; Charles M. Marson (2001). "Dimethylchloromethyleneammonium Chloride". Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rd319m. ISBN 0-471-93623-5.
- ^ Jones, G.; Stanforth, S. P. (2000). "The Vilsmeier Reaction of Non-Aromatic Compounds". Org. React. 56 (2): 355–686. doi:10.1002/0471264180.or056.02.









You must be logged in to post a comment.