The Bobbitt reaction is a name reaction in organic chemistry. It is named after the American chemist James M. Bobbitt.[1] The reaction allows the synthesis of 1-, 4-, and N-substituted 1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinolines and also 1-, and 4-substituted isoquinolines.
General Reaction Scheme
The reaction scheme below shows the synthesis of 1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline from benzaldehyde and 2,2-diethylethylamine.[1]
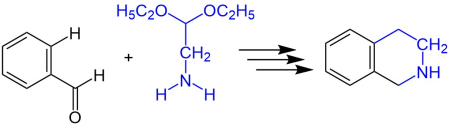
Reaction Mechanism
A possible mechanism is depicted below:[1]

First the benzaliminoacetal 3 is built by the condensation of benzaldehyde 1 and 2,2-diethylethylamine 2. After the condensation the C=N-double bond in 3 is hydrogenated to form 4. Subsequently, an ethanol is removed. Next, the compound 5 is built including the cyclization step. After that the C=C-double bond in 5 is hydrogenated . Thus, 1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline 6 is formed.
Applications
The Bobbitt reaction has found application in the preparation of some alkaloids[1] such as carnegine,[2] lophocerine, salsolidine,[2] and salsoline.[2]
See also
References
- ^ a b c d Wang, Zerong (2009). Comprehensive organic name reactions and reagents. Hoboken, N.J.: John Wiley. pp. 441–444. ISBN 978-0-471-70450-8.
- ^ a b c Bobbitt, James M.; Roy, Dibyendu Nath; Marchand, Anthony; Allen, Christopher Whitney (1967). "Synthesis of isoquinolines. VI. N-alkyl-1,2,4-tetrahydroisoquinolines". J. Org. Chem. 32 (7): 2225–2227. doi:10.1021/jo01282a030..









You must be logged in to post a comment.