Acokanthera is a genus of flowering plants in the family Apocynaceae. It comprises 5 species and is generally restricted to Africa, although A. schimperi also occurs in Yemen.[1] Its sap contains the deadly toxin ouabain, a glycoside that causes heart failure. The sap is among the most commonly used in arrow poisons,[2][3] including those used for poaching elephants.[4]
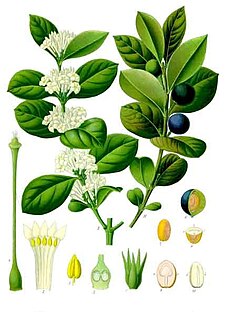
from Köhler's Medizinal Pflanzen 1897
The poison it contains works by stopping the heart, like most other arrow poisons.[5]
- Species[1]
- Acokanthera laevigata Kupicha - Tanzania, Malawi
- Acokanthera oblongifolia (Hochst.) Benth. & Hook.f. ex B.D.Jacks. - Mozambique, South Africa
- Acokanthera oppositifolia (Lam.) Codd - widespread from Cape Province north to Zaire and Tanzania
- Acokanthera rotundata (Codd) Kupicha - Zimbabwe, Eswatini, eastern South Africa
- Acokanthera schimperi (A.DC.) Schweinf. - Yemen, Eritrea, Djibouti, Ethiopia, Somalia, Socotra, Kenya, Tanzania, Rwanda, Zaire
References
- ^ a b c Kew World Checklist of Selected Plant Families
- ^ Gould, George M. (1905). Dictionary of New Medical Terms. London: Bailliere Tindall & Cox. pp. 36.
poison.
- ^ Schmelzer, G.H. & Gurib-Fakim, A. (Editors), 2008. Plant Resources of Tropical Africa 11(1). Medicinal plants 1. PROTA Foundation, Wageningen, Netherlands / Backhuys Publishers, Leiden, Netherlands / CTA, Wageningen, Netherlands. 791 pp.
- ^ Kinloch, Bruce (1988). The Shamba Raiders. Hampshire: Ashford. pp. 21. ISBN 1852530359.
- ^ Stewart, Amy (2009). Wicked Plants. p. 5.









You must be logged in to post a comment.