Portal:World
The World Portal

The world is the totality of entities, the whole of reality, or everything that exists. The nature of the world has been conceptualized differently in different fields. Some conceptions see the world as unique, while others talk of a "plurality of worlds". Some treat the world as one simple object, while others analyze the world as a complex made up of parts.
In scientific cosmology, the world or universe is commonly defined as "the totality of all space and time; all that is, has been, and will be". Theories of modality talk of possible worlds as complete and consistent ways how things could have been. Phenomenology, starting from the horizon of co-given objects present in the periphery of every experience, defines the world as the biggest horizon, or the "horizon of all horizons". In philosophy of mind, the world is contrasted with the mind as that which is represented by the mind.
Theology conceptualizes the world in relation to God, for example, as God's creation, as identical to God, or as the two being interdependent. In religions, there is a tendency to downgrade the material or sensory world in favor of a spiritual world to be sought through religious practice. A comprehensive representation of the world and our place in it, as is found in religions, is known as a worldview. Cosmogony is the field that studies the origin or creation of the world, while eschatology refers to the science or doctrine of the last things or of the end of the world.
In various contexts, the term "world" takes a more restricted meaning associated, for example, with the Earth and all life on it, with humanity as a whole, or with an international or intercontinental scope. In this sense, world history refers to the history of humanity as a whole, and world politics is the discipline of political science studying issues that transcend nations and continents. Other examples include terms such as "world religion", "world language", "world government", "world war", "world population", "world economy", or "world championship". (Full article...)
Selected articles - show another
-
Image 1The term "new world order" refers to a new period of history evidencing dramatic change in world political thought and the balance of power in international relations. Despite varied interpretations of this term, it is commonly associated with the notion of world governance.
The phrase "new world order" or similar language was used in the period toward the end of the First World War in relation to Woodrow Wilson's vision for international peace; Wilson called for a League of Nations to prevent aggression and conflict. In some instances when Franklin D. Roosevelt used the phrase "new world order", or "new order in the world" it was to refer to Axis powers plans for world domination. Although Roosevelt and Harry S. Truman may have been hesitant to use the phrase, commentators have applied the term retroactively to the order put in place by the World War II victors including the United Nations and the Bretton Woods system as a "new world order." (Full article...) -
Image 2

Second preliminary session of the World Summit Information Society, plenary meeting, 18–25 February 2005, UN building, Geneva, Switzerland.
The World Summit on the Information Society (WSIS) was a two-phase United Nations-sponsored summit on information, communication and, in broad terms, the information society that took place in 2003 in Geneva and in 2005 in Tunis. WSIS Forums have taken place periodically since then. One of the Summit's chief aims is to bridge the global digital divide separating rich countries from poor countries by increasing internet accessibility in the developing world. The conferences established 17 May as World Information Society Day.
The WSIS+10 Process marked the ten-year milestone since the 2005 Summit. In 2015, the stocktaking process culminated with a High-Level meeting of the UN General Assembly on 15 and 16 December in New York. The United Nations General Assembly will conclude the WSIS+20 review in December 2025. (Full article...) -
Image 3

The Hereford mappa mundi, a map of the world with Jerusalem at its centre
The Hereford Mappa Mundi (Latin: mappa mundi, map of the world) is the largest medieval map still known to exist, depicting the known world. It is a religious rather than literal depiction, featuring heaven, hell and the path to salvation. Dating from c. 1300 AD, the map is drawn in a form deriving from the T and O pattern. It is displayed at Hereford Cathedral in Hereford, England. The map was created as an intricate work of art rather than as a navigational tool. Sources for the information presented on the map include the Alexander tradition, medieval bestiaries and legends of monstrous races, as well as the Bible.
Although the evidence is circumstantial, recent work links the map with the promotion of the cult of Thomas de Cantilupe. Others link the map to a justification of the expulsion of Jewry from England. Potentially antisemitic images include a horned Moses and a depiction of Jews worshipping the Golden Calf in the form of a Saracen devil. The map may also reflect very patriarchal views of women as inherently sinful, including figures such as the wife of Lot being turned into a pillar of salt for gazing at the city of Sodom. Cantilupe was known for his dislike of Jews; in historian Debra Strickland's opinion he was regarded as misogynistic even by the standards of his own time. (Full article...) -
Image 4

UN Trade and Development (UNCTAD) is an intergovernmental organization within the United Nations Secretariat that promotes the interests of developing countries in world trade. It was established in 1964 by the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) as the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development but rebranded to its current name on the occasion of its 60th anniversary in 2024. It reports to both the General Assembly and the United Nations Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC). UNCTAD is composed of 195 member states and works with non-governmental organizations worldwide; its permanent secretariat is at UNOG in Geneva, Switzerland.
The primary objective of UNCTAD is to formulate policies relating to all aspects of development, including trade, aid, transport, finance and technology. It was created in response to concerns among developing countries that existing international institutions like GATT (since replaced by the World Trade Organization), the International Monetary Fund (IMF), and the World Bank were not properly organized to handle the particular problems of developing countries; UNCTAD would provide a forum where developing nations could discuss and address problems relating to their economic development. (Full article...) -
Image 5

The Arab world (Arabic: اَلْعَالَمُ الْعَرَبِيُّ al-ʿālam al-ʿarabī), formally the Arab homeland (اَلْوَطَنُ الْعَرَبِيُّ al-waṭan al-ʿarabī), also known as the Arab nation (اَلْأُمَّةُ الْعَرَبِيَّةُ al-ummah al-ʿarabiyyah), the Arabsphere, or the Arab states, comprises a large group of countries, mainly located in West Asia and North Africa. While the majority of people in the Arab world are ethnically Arab, there are also significant populations of other ethnic groups such as Berbers, Kurds, Somalis and Nubians, among other groups. Arabic is used as the lingua franca throughout the Arab world.
The Arab world is at its minimum defined as the 19 states where Arabs form at least a plurality of the population. At its maximum it consists of the 22 members of the Arab League, an international organization, which on top of the 19 plurality Arab states also includes the Bantu-speaking Comoros, and the Cushitic-speaking Djibouti and Somalia. The region stretches from the Atlantic Ocean in the west to the Arabian Sea in the east, and from the Mediterranean Sea in the north to the Indian Ocean in the southeast. The eastern part of the Arab world is known as the Mashriq, and the western part as the Maghreb. (Full article...) -
Image 6

The map of the mouth of the River Amazon
The International Map of the World (IMW; also the Millionth Map of the World, after its scale of 1:1 000 000) was a project to create a complete map of the world according to internationally agreed standards. It was first proposed by the German geographer Albrecht Penck in 1891.
The Central Bureau of the Map of the World was established in London. After the Second World War, UNESCO took over the project. By 1953, 400 sheets had been produced. The completed sheets became outdated before the project had produced a full set of maps, and by the 1960s was being dismissed as being of no practical use. The project was no longer monitored by the 1990s. (Full article...) -
Image 7

Map of Pangaea around 250 million years ago, at the beginning of the Triassic
Pangaea or Pangea (/pænˈdʒiːə/ pan-JEE-ə) was a supercontinent that existed during the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic eras. It assembled from the earlier continental units of Gondwana, Euramerica and Siberia during the Carboniferous period approximately 335 million years ago, and began to break apart about 200 million years ago, at the end of the Triassic and beginning of the Jurassic. Pangaea was C-shaped, with the bulk of its mass stretching between Earth's northern and southern polar regions and surrounded by the superocean Panthalassa and the Paleo-Tethys and subsequent Tethys Oceans. Pangaea is the most recent supercontinent to have existed and was the first to be reconstructed by geologists. (Full article...)
General images - load new batch
-
Image 1Artist's conception of Hadean Eon Earth, when it was much hotter and inhospitable to all forms of life. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 2Earth's axial tilt causing different angles of seasonal illumination at different orbital positions around the Sun (from Earth)
-
Image 3Chloroplasts in the cells of a moss (from History of Earth)
-
Image 4Japanese depiction of a Portuguese carrack, a result of globalizing maritime trade
-
Image 5Change in average surface air temperature and drivers for that change. Human activity has caused increased temperatures, with natural forces adding some variability. (from Earth)
-
Image 6A computer-generated image mapping the prevalence of artificial satellites and space debris around Earth in geosynchronous and low Earth orbit (from Earth)
-
Image 7Artist's impression of a Hadean landscape with the relatively newly formed Moon still looming closely over Earth and both bodies sustaining strong volcanism. (from History of Earth)
-
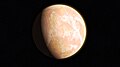
Image 11The pale orange dot, an artist's impression of the early Earth which might have appeared orange through its hazy methane rich prebiotic second atmosphere. Earth's atmosphere at this stage was somewhat comparable to today's atmosphere of Titan. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 14The replicator in virtually all known life is deoxyribonucleic acid. DNA is far more complex than the original replicator and its replication systems are highly elaborate. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 15Notre-Dame de Paris, France
-
Image 16Artist's impression of the enormous collision that probably formed the Moon (from History of Earth)
-
Image 17Geologic map of North America, color-coded by age. From most recent to oldest, age is indicated by yellow, green, blue, and red. The reds and pinks indicate rock from the Archean.
-
Image 18Fall of the Berlin Wall, 1989
-
Image 20Earth's history with time-spans of the eons to scale. Ma means "million years ago", Ga means "billion years ago". (from History of Earth)
-
Image 22Obelisk of Axum, Ethiopia
-
Image 23An artist's impression of ice age Earth at glacial maximum. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 24Yggdrasil, an attempt to reconstruct the Norse world tree which connects the heavens, the world, and the underworld. (from World)
-
Image 25Vitruvian Man, c. 1490 by Leonardo da Vinci, epitomizes the advances in art and science seen during the Renaissance. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 27Atomic bombing of Nagasaki, 1945
-
Image 28Lithified stromatolites on the shores of Lake Thetis, Western Australia. Archean stromatolites are the first direct fossil traces of life on Earth. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 29Angkor Wat temple complex, Cambodia, early 12th century
-
Image 31The first airplane, the Wright Flyer, flew on 17 December 1903.
-
Image 33Shanghai. China urbanized rapidly in the 21st century.
-
Image 34Battle during the 1281 Mongol invasion of Japan
-
Image 35Artist's rendition of an oxinated fully-frozen Snowball Earth with no remaining liquid surface water. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 38A composite image of Earth, with its different types of surface discernible: Earth's surface dominating Ocean (blue), Africa with lush (green) to dry (brown) land and Earth's polar ice in the form of Antarctic sea ice (grey) covering the Antarctic or Southern Ocean and the Antarctic ice sheet (white) covering Antarctica. (from Earth)
-
Image 39Trilobites first appeared during the Cambrian period and were among the most widespread and diverse groups of Paleozoic organisms. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 41A map of heat flow from Earth's interior to the surface of Earth's crust, mostly along the oceanic ridges (from Earth)
-
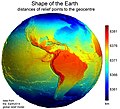
Image 42Earth's western hemisphere showing topography relative to Earth's center instead of to mean sea level, as in common topographic maps (from Earth)
-
Image 44Dinosaurs were the dominant terrestrial vertebrates throughout most of the Mesozoic (from History of Earth)
-
Image 46Benin Bronze head from Nigeria
-
Image 47An impression of the Archean, the eon after Earth's formation, featuring round stromatolites, which are early oxygen-producing forms of life from billions of years ago. After the Late Heavy Bombardment, Earth's crust had cooled, its water-rich barren surface is marked by continents and volcanoes, with the Moon still orbiting Earth half as far as it is today, appearing 2.8 times larger and producing strong tides. (from Earth)
-
Image 50A reconstruction of human history based on fossil data. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 51A banded iron formation from the 3.15 Ga Moodies Group, Barberton Greenstone Belt, South Africa. Red layers represent the times when oxygen was available; gray layers were formed in anoxic circumstances. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 52Pale orange dot, an impression of Early Earth, featuring its tinted orange methane-rich early atmosphere (from Earth)
-
Image 53A view of Earth with its global ocean and cloud cover, which dominate Earth's surface and hydrosphere; at Earth's polar regions, its hydrosphere forms larger areas of ice cover. (from Earth)
-
Image 55A pillar at Neolithic Göbekli Tepe
-
Image 56Last Moon landing: Apollo 17 (1972)
-
Image 58A view of Earth with different layers of its atmosphere visible: the troposphere with its clouds casting shadows, a band of stratospheric blue sky at the horizon, and a line of green airglow of the lower thermosphere around an altitude of 100 km, at the edge of space (from Earth)
-
Image 60Pangaea was a supercontinent that existed from about 300 to 180 Ma. The outlines of the modern continents and other landmasses are indicated on this map. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 61Graph showing range of estimated partial pressure of atmospheric oxygen through geologic time (from History of Earth)
-
Image 6213th-century French historiated initial with the three classes of medieval society: those who prayed (the clergy), those who fought (the knights), and those who worked (the peasantry)
-
Image 64Cuneiform inscription, eastern Turkey
-
Image 65A 580 million year old fossil of Spriggina floundensi, an animal from the Ediacaran period. Such life forms could have been ancestors to the many new forms that originated in the Cambrian Explosion. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 67Tiktaalik, a fish with limb-like fins and a predecessor of tetrapods. Reconstruction from fossils about 375 million years old. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 69Earth's land use for human agriculture in 2019 (from Earth)
-
Image 70A depiction of the early Solar System's protoplanetary disk from which Earth and other Solar System bodies were formed (from Earth)
-
Image 71One of the eleven Rock-hewn Churches of Lalibela constructed during the Zagwe dynasty in Ethiopia (from Human history)
-
Image 72Artist's impression of Earth during the later Archean, the largely cooled planetary crust and water-rich barren surface, marked by volcanoes and continents, features already round microbialites. The Moon, still orbiting Earth much closer than today and still dominating Earth's sky, produced strong tides. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 73Tracy Caldwell Dyson, a NASA astronaut, observing Earth from the Cupola module at the International Space Station on 11 September 2010 (from Earth)
-
Image 74A reconstruction of Pannotia (550 Ma). (from History of Earth)
-
Image 75Standing Buddha from Gandhara, 2nd century CE
-
Image 76Olmec colossal head, now at the Museo de Antropología de Xalapa
-
Image 79Successive dispersals of Homo erectus (yellow), Homo neanderthalensis (ochre) during Out of Africa I and Homo sapiens (red, Out of Africa II), with the numbers of years since they appeared before present. (from Human history)
-
Image 80Earth's night-side upper atmosphere appearing from the bottom as bands of afterglow illuminating the troposphere in orange with silhouettes of clouds, and the stratosphere in white and blue. Next the mesosphere (pink area) extends to the orange and faintly green line of the lowest airglow, at about one hundred kilometers at the edge of space and the lower edge of the thermosphere (invisible). Continuing with green and red bands of aurorae stretching over several hundred kilometers. (from Earth)
-
Image 81Portrait of Alfraganus in the Compilatio astronomica, 1493. Islamic astronomers began just before the 9th century to collect and translate Indian, Persian and Greek astronomical texts, adding their own astronomy and enabling later, particularly European astronomy to build on. Symbolic for the post-classical period, a period of an increasing trans-regional literary culture, particularly in the sciences, spreading and building on methods of science. (from Human history)
-
Image 82An animation of the changing density of productive vegetation on land (low in brown; heavy in dark green) and phytoplankton at the ocean surface (low in purple; high in yellow) (from Earth)
-
Image 84A schematic view of Earth's magnetosphere with solar wind flowing from left to right (from Earth)
-
Image 85Great Pyramids of Giza, Egypt
Megacities of the world - show another
Tianjin is a major international port city in China. It is a direct-administered municipality on the shore of the Bohai Sea making it separate from the surrounding Hebei province. It is one of the nine national central cities, with a total population of 13,866,009 inhabitants at the time of the 2020 Chinese census. Its metropolitan area, which is made up of 12 central districts (other than Baodi, Jizhou, Jinghai and Ninghe), was home to 11,165,706 inhabitants in 2015 and is also the world's 29th-largest agglomeration (between Chengdu and Rio de Janeiro) and 11th-most populous city proper.
Tianjin is governed as one of the four municipalities (alongside Beijing, Shanghai, and Chongqing) under the direct administration of the State Council of China. However, it is the only municipality with a population of less than 20 million. The city borders Hebei Province and Beijing Municipality, bounded to the east by the Bohai Gulf portion of the Yellow Sea. Part of the Bohai Economic Rim, it is the largest coastal city in Northern China and part of the Jing-Jin-Ji megapolis. (Full article...)
Did you know - load new batch

- ... that one night on the planet Venus lasts just over 58 full days on Earth?
- ... that Alda Milner-Barry, the older sister of World War II Enigma codebreaker Stuart Milner-Barry, worked for British military intelligence during World War I?
- ... that the 2023 US FIBA Basketball World Cup team is the first American national team of NBA players without an All-NBA player?
- ... that Frederick Perceval, 11th Earl of Egmont, was nicknamed "the loneliest boy in the world" by journalists?
- ... that fictional planets of the Solar System include planets between Venus and Earth, planets on the inside of a hollow Earth, and a planet "behind the Earth"?
- ... that Jackson Cantwell, the number-one college football recruit for 2026, is the son of two Olympians and holds several youth world records in track and field?
- ... that Fritz Strassmann, a co-discoverer of nuclear fission, concealed a Jewish woman in his home during World War II?
- ... that during the Second World War the British government transmitted German music to Nazi U-boats?
Countries of the world - show another

Chad, officially the Republic of Chad, is a landlocked country in Central Africa. It is bordered by Libya to the north, Sudan to the east, the Central African Republic to the south, Cameroon to the southwest, Nigeria to the southwest (at Lake Chad), and Niger to the west. Chad has a population of 19 million, of which 1.6 million live in the capital and largest city of N'Djamena. With a total area of around 1,300,000 km2 (500,000 sq mi), Chad is the fifth-largest country in Africa and the twentieth largest nation by area.
Chad has several regions: the Sahara desert in the north, an arid zone in the centre known as the Sahel, and a more fertile Sudanian Savanna zone in the south. Lake Chad, after which the country is named, is the second-largest wetland in Africa. Chad's official languages are Arabic and French with most education and state documents being in French. It is home to over 200 ethnic and linguistic groups. Islam (55.1%) and Christianity (41.1%) are the main religions practiced in Chad. (Full article...)
The Seven Wonders of Canada was a 2007 competition sponsored by CBC Television's The National and CBC Radio One's Sounds Like Canada. They sought to determine Canada's "seven wonders" by receiving nominations from viewers, and then from on-line voting of the short list. After the vote, a panel of judges, Ra McGuire, Roy MacGregor and Roberta L. Jamieson, picked the winners based on geographic and poetic criteria. Their seven picks were revealed on The National on June 7, 2007, making the official Seven Wonders of Canada, the Canoe, the Igloo, Niagara Falls, Old Quebec City, Pier 21 Halifax, Prairie Skies, and the Rockies. CBC anchor Peter Mansbridge commented on the top winner, “it’s hard to imagine Canada being Canada without the canoe. Explorers, missionaries, fur traders and First Nations—they’re all linked by this subtle and simple craft. To many, the quintessential Canadian experience begins by picking up a paddle. That’s why the canoe is one of the seven wonders” (Osler 2014). There were over 25,000 nominations and 1 million votes cast, according to the CBC website. The top audience votes were the Sleeping Giant, Niagara Falls, the Bay of Fundy, Nahanni National Park Reserve, the Northern Lights, the Rockies, and the Cabot Trail. The CBC website has a dedicated section for the Seven Wonders of Canada (https://www.cbc.ca/sevenwonders/index.html). (Full article...)
Related portals
Protected areas of the world - load new batch
-
Image 1

Rano Kau, Parque National Rapa Nui, Easter Island
The protected areas of Chile are areas that have natural beauty or significant historical value protected by the government of Chile. These protected areas cover over 140,000 km2 (54,054 sq mi), which is 19% of the territory of Chile. The National System of Protected Wild Areas (SNASPE by its Spanish acronym) is regulated by law #18,362 passed in 1984, and administered by the National Forest Corporation (CONAF).
There are three types of territories: (Full article...) -
Image 2The protected areas of South Africa include national parks and marine protected areas managed by the national government, public nature reserves managed by provincial and local governments, and private nature reserves managed by private landowners. Most protected areas are intended for the conservation of flora and fauna. National parks are maintained by South African National Parks (SANParks). A number of national parks have been incorporated in transfrontier conservation areas.
Protected areas may also be protected for their value and importance as historical, cultural heritage or scientific sites. More information on these can be found in the list of heritage sites in South Africa. (Full article...) -
Image 3

Network of protected areas in Albania (2020)
Despite being a relatively small country, Albania is exceedingly rich in biodiversity. Its ecosystems and habitats support over 5,550 species of vascular and non-vascular plants and more than 15,600 species of coniferous and non-coniferous evergreens, most of which are threatened at global and European levels. The country has made recent efforts to expand its network of protected areas which now include: 11 national parks, 1 marine park, 718 nature monuments, 23 managed nature reserves, 11 protected landscapes, 4 World Heritage Sites, 4 Ramsar sites and other protected areas of various categories, that when combined, account for 21.36% of the territory. Furthermore, a biosphere reserve, 45 important plant areas and 16 important bird areas are found in the country.
Meanwhile, the central government has proclaimed the Coastline and the Tirana Greenbelt as areas of national importance. (Full article...) -
Image 4

Tijuca Forest National Park
Protected areas of Brazil included various classes of area according to the National System of Nature Conservation Units (SNUC), a formal, unified system for federal, state and municipal parks created in 2000. (Full article...) -
Image 5
Mombacho Volcano Natural Reserve
The protected areas of Nicaragua are areas that have natural beauty or significance and are protected by Nicaragua. Nicaragua has 78 protected areas that cover 22,422 km2, about 17.3% of the nations landmass. The National System of Protected Areas (SINAP) is administered by the Ministry of the Environment and Natural Resources (MARENA). (Full article...) -
Image 6
-
Image 7The Australian Capital Territory as of 2014 contains 46 separate protected areas with a total land area of 1,302 km2 (503 sq mi) or 55.5% of the territory's area, and which managed by Territory and Municipal Services of the ACT government: (Full article...)
-
Image 8

Emerald Network of Ukraine [uk] in 2019, the Ukrainian equivalent of Natura 2000, both part of the Emerald network of the Berne Convention on the Conservation of European Wildlife and Natural Habitats.
Protected areas of Ukraine (Ukrainian: охоронні території) are special areas of Ukraine established with the goal of protecting the natural and cultural heritage of the country from excessive changes as a result of human activity. The protection of the areas is the responsibility of the government of Ukraine, specifically the Cabinet of Ministers of Ukraine.
Ukraine has several categories of protected areas of Ukraine and the protected areas include: (Full article...) -
Image 9
Grand Canyon of Yellowstone
The protected areas of the United States are managed by an array of different federal, state, tribal and local level authorities and receive widely varying levels of protection. Some areas are managed as wilderness, while others are operated with acceptable commercial exploitation. As of 2022, the 42,826 protected areas covered 1,235,486 km2 (477,024 sq mi), or 13 percent of the land area of the United States. This is also one-tenth of the protected land area of the world. The U.S. also had a total of 871 National Marine Protected Areas, covering an additional 1,240,000 mi2 (3,200,000 km2), or 26 percent of the total marine area of the United States. (Full article...) -
Image 10

The mountain of Stob Binnein lies in the Loch Lomond and The Trossachs National Park.
Many parts of Scotland are protected in accordance with a number of national and international designations because of their environmental, historical or cultural value. Protected areas can be divided according to the type of resource which each seeks to protect. NatureScot has various roles in the delivery of many environmental designations in Scotland, i.e. those aimed at protecting flora and fauna, scenic qualities and geological features. Historic Environment Scotland is responsible for designations that protect sites of historic and cultural importance. Some international designations, such as World Heritage Sites, can cover both categories of site.
The various designations overlap considerably with many protected areas being covered by multiple designations with different boundaries. (Full article...) -
Image 11This is a list of protected areas of Sierra Leone, including national parks, game reserves, conservation areas, wetlands, and those that are listed as proposed protected areas in the UN Environment Programme World Conservation Monitoring Centre (UNEP WCM) database. (Full article...)
-
Image 12Protected areas of Indonesia comprise both terrestrial and marine environments in any of the six IUCN Protected Area categories. There are over 500 protected areas in Indonesia, of which 57 National Parks and another nature and game reserves cover overall 36.1 million ha land area. The total protected land area represents over 18.9% of Indonesia's landmass.Marine Protected Areas comprise over 28.4 million ha (around 9% of Indonesian territorial waters). (Full article...)
-
Image 13Protected areas of Canada consist of approximately 12.1 percent of the nation's landmass and freshwater are considered conservation areas, including 11.4 percent designated as protected areas. Approximately 13.8 percent of Canada's territorial waters are conserved, including 8.9 percent designated as protected areas. Terrestrial areas conserved have increased by 65 percent in the 21st century, while marine areas conserved have increased by more than 3,800 percent.
Conservation and protected areas have different mandates depending on the organization which manages them, with some areas having a greater focus on ecological integrity, historical preservation, public usage, scientific research, or a combination of usages. Some areas such as the Polar Bear Pass, are co-managed and overseen by government and local indigenous agencies. (Full article...) -
Image 14A National Biodiversity Conservation Area (NBCA) is an environmentally protected area in Laos. There are altogether 21 different NBCAs in Laos, protecting 29,775 square kilometers. Another 10 NBCAs have been proposed, the territory of many of them being treated by authorities as though they were already officially protected. (Full article...)
-
Image 15Protected areas of Norway include:
About 17 percent of the mainland of Norway is protected. Of this, ca. 8.3 percent is national parks, 1.3 percent is nature reserves and 4.7 percent otherwise protected. (Full article...)
Selected world maps
-
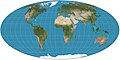
Image 1The Goode homolosine projection is a pseudocylindrical, equal-area, composite map projection used for world maps.
-
Image 21516 map of the world by Martin Waldseemüller
-
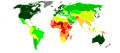
Image 3United Nations Human Development Index map by country (2016)
-
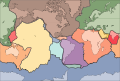
Image 4A plate tectonics map with volcano locations indicated with red circles
-
Image 5Time zones of the world
-
Image 6Only a few of the largest large igneous provinces appear (coloured dark purple) on this geological map, which depicts crustal geologic provinces as seen in seismic refraction data
-
Image 7Mollweide projection of the world
-
Image 8Index map from the International Map of the World (1:1,000,000 scale)
-
Image 9The world map by Gerardus Mercator (1569), the first map in the well-known Mercator projection
World records
- List of Olympic records in athletics
- List of world records in athletics
- List of junior world records in athletics
- List of world records in masters athletics
- List of world youth bests in athletics
- List of IPC world records in athletics
- List of world records in canoeing
- List of world records in chess
- List of cycling records
- List of world records in track cycling
- List of world records in finswimming
- List of world records in juggling
- List of world records in rowing
- List of world records in speed skating
- List of world records in swimming
- List of IPC world records in swimming
- List of world records in Olympic weightlifting
Topics
Continents of Earth | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||
| ||||||||
| ||||||||
| Cenozoic Era (present–66.0 Ma) |
| ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mesozoic Era (66.0–252 Ma) |
| ||||||||||||
| Paleozoic Era (252–539 Ma) |
| ||||||||||||
| Proterozoic Eon (539 Ma–2.5 Ga) |
| ||||||||||||
| Archean Eon (2.5–4 Ga) | |||||||||||||
| Hadean Eon (4–4.6 Ga) | |||||||||||||
ka = kiloannum (thousand years ago); Ma = megaannum (million years ago); Ga = gigaannum (billion years ago). See also: Geologic time scale • | |||||||||||||
| City proper | |
|---|---|
| Metropolitan area | |
| Urban area/agglomeration | |
| Historical | |
| Related articles | |
| Locations | ||
|---|---|---|
| Related | ||
| Retrospectively recognized expositions | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BIE-recognized Universal expositions | |||||||||||||
| BIE-recognized specialized expositions |
| ||||||||||||
| BIE-recognized horticultural exhibitions (AIPH) | |||||||||||||
| Not BIE- recognized |
| ||||||||||||
†Postponed to 2021 due to the COVID-19 pandemic | |||||||||||||
| Confederations | |
|---|---|
| World Championships | |
| World Cup | |
| Special events | |
| Presidents |
|
| Awards | |
| |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
Economic classification of countries | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Three-World Model | |||||
| Gross domestic product (GDP) |
| ||||
| Gross national income (GNI) | |||||
| Wages | |||||
| Wealth | |||||
| Other national accounts | |||||
| Human development | |||||
| Digital divide | |||||
| Net international investment position (NIIP) | |||||
| Technological |
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sociological | |||||
| Ecological |
| ||||
| Biological |
| ||||
| Astronomical | |||||
| Eschatological |
| ||||
| Others |
| ||||
| Fictional | |||||
| Organizations | |||||
| Theatres |
| ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Principal participants |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Timeline |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Aspects |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| General |
| ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Participants |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Timeline |
| ||||||||||||||||
Categories
Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
 Commons
Commons
Free media repository -
 Wikibooks
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
 Wikidata
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
 Wikinews
Wikinews
Free-content news -
 Wikiquote
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
 Wikisource
Wikisource
Free-content library -
 Wikispecies
Wikispecies
Directory of species -
 Wikiversity
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
 Wikivoyage
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
 Wiktionary
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus